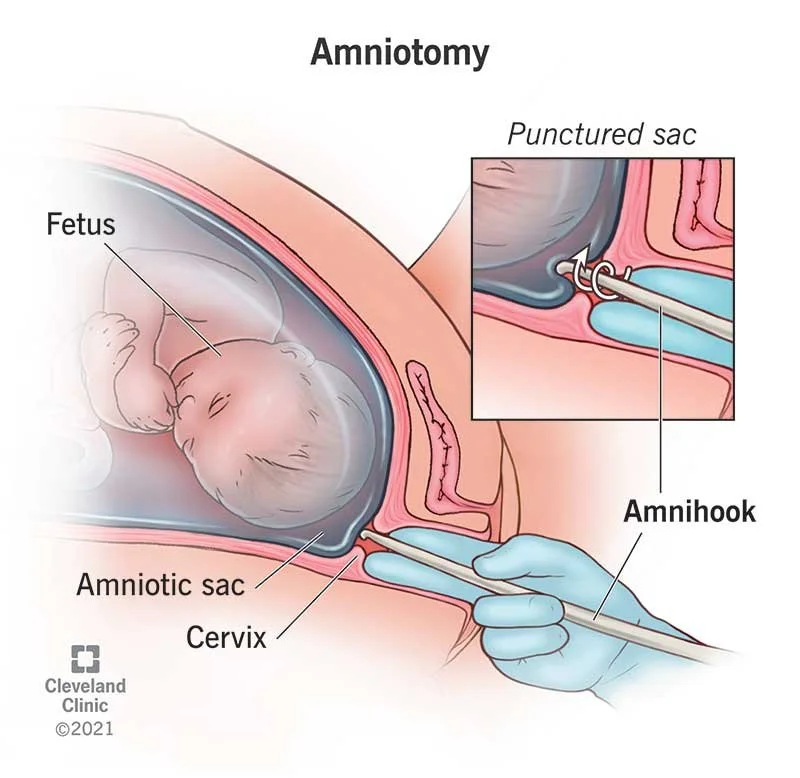
Artificial rupture of membranes (AROM)
Amniotomy, also known as artificial rupture of membranes (AROM), is a medical procedure in which the healthcare provider uses a specialized tool called an amnihook to break the amniotic sac (bag of waters) during labor. The amniotic sac is the fluid-filled membrane that surrounds and protects the developing fetus during pregnancy.
Amniotomy is typically performed in a hospital setting and is used to help speed up labor or to induce labor when it has not started on its own. It can also be done to allow for fetal monitoring or to collect a sample of amniotic fluid for testing.
While amniotomy is drug-free and generally not painful it does carry some risks. These include infection, prolapse of the umbilical cord, and fetal distress. As with any medical procedure, it is important to discuss the risks and benefits of amniotomy with your healthcare provider before making a decision.
Remember:
You can always say no, and allow water to rupture on its own. You have a right to refuse a procedure.
There are other natural and medical options to induce and shorten labor if that’s what you would like.
If you don’t want AROM, let your healthcare provider know before they do a cervical exam. Many times, they will rupture your waters without asking first.